diff --git a/content/cn/open_source/modules/memories/naive_textual_memory.md b/content/cn/open_source/modules/memories/naive_textual_memory.md
index 699ac068..779863af 100644
--- a/content/cn/open_source/modules/memories/naive_textual_memory.md
+++ b/content/cn/open_source/modules/memories/naive_textual_memory.md
@@ -1,13 +1,12 @@
---
title: "NaiveTextMemory: 简单明文记忆"
-desc: "MemOS 中最轻量级的记忆模块,专为快速原型开发和简单场景设计。无需向量数据库,使用关键词匹配即可快速检索。"
+desc: "MemOS 中最轻量级的记忆模块,专为快速原型开发和简单场景设计。无需向量数据库,使用关键词匹配即可快速检索。让我们用最简单的方式开始使用 MemOS 记忆系统!
+`NaiveTextMemory` 是一个基于内存的明文记忆模块,将记忆存储在内存列表中,使用关键词匹配进行检索。它是学习 MemOS 的最佳起点,也适用于演示、测试和小规模应用。"
+
---
-# NaiveTextMemory: 简单明文记忆
-让我们用最简单的方式开始使用 MemOS 记忆系统!
-`NaiveTextMemory` 是一个轻量级、基于内存的明文记忆模块,将记忆存储在内存列表中,使用关键词匹配进行检索。它是学习 MemOS 的最佳起点,也适用于演示、测试和小规模应用。
## 目录
@@ -144,7 +143,7 @@ memory = NaiveTextMemory(config: NaiveTextMemoryConfig)
-::alert{type="info"}
+::note
**示例对比**
查询:"猫咪"
- **关键词匹配**:只匹配包含"猫"、"猫咪"的记忆
diff --git a/content/cn/open_source/modules/memories/tree_textual_memory.md b/content/cn/open_source/modules/memories/tree_textual_memory.md
index 9eed3db9..8b8e42ed 100644
--- a/content/cn/open_source/modules/memories/tree_textual_memory.md
+++ b/content/cn/open_source/modules/memories/tree_textual_memory.md
@@ -1,12 +1,13 @@
---
title: "TreeTextMemory: 分层结构的明文记忆"
----
-
-让我们在MemOS中构建你的第一个**基于图的、树形明文记忆**!
+desc: "让我们在MemOS中构建你的第一个**基于图的、树形明文记忆**!
**TreeTextMemory** 支持以结构化方式组织、关联并检索记忆,同时保留丰富的上下文信息与良好的可解释性。
-MemOS当前使用[Neo4j](/open_source/modules/memories/neo4j_graph_db)作为后端,未来计划支持更多图数据库。
+MemOS当前使用[Neo4j](/open_source/modules/memories/neo4j_graph_db)作为后端,未来计划支持更多图数据库。"
+---
+
+
## 目录
diff --git a/content/cn/open_source/open_source_api/chat/chat.md b/content/cn/open_source/open_source_api/chat/chat.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..924aa8c1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/content/cn/open_source/open_source_api/chat/chat.md
@@ -0,0 +1,86 @@
+---
+title: 对话
+desc: 集成“检索、生成、存储”全链路的 RAG 闭环接口,支持基于 MemCube 的个性化回复与记忆自动沉淀。
+---
+
+:::note
+有关API字段、格式等信息的完整列表,详见[Chat 接口文档](/api_docs/chat/chat)。
+:::
+
+**接口路径**:
+* **全量响应**:`POST /product/chat/complete`
+* **流式响应 (SSE)**:`POST /product/chat/stream`
+
+**功能描述**:本接口是 MemOS 的核心业务编排入口。它能够自动从指定的 `readable_cube_ids` 中召回相关记忆,结合当前语境生成回复,并可选地将对话结果自动回写至 `writable_cube_ids` 中,实现 AI 应用的自我进化。
+
+
+## 1. 核心架构:ChatHandler 编排流程
+
+1. **记忆检索 (Retrieval)**:根据 `readable_cube_ids` 调用 **SearchHandler**,从隔离的 Cube 中提取相关的事实、偏好及工具背景。
+2. **上下文增强生成 (Generation)**:将检索到的记忆片段注入 Prompt,调用指定的 LLM(通过 `model_name_or_path`)生成针对性回复。
+3. **记忆自动闭环 (Storage)**:若开启 `add_message_on_answer=true`,系统会调用 **AddHandler** 将本次对话异步存入指定的 Cube,无需开发者手动调用添加接口。
+## 2. 关键接口参数
+
+### 2.1 身份与语境
+| 参数名 | 类型 | 必填 | 说明 |
+| :--- | :--- | :--- | :--- |
+| **`query`** | `str` | 是 | 用户当前的提问内容。 |
+| **`user_id`** | `str` | 是 | 用户唯一标识,用于鉴权与数据隔离。 |
+| `history` | `list` | 否 | 短期历史对话记录,用于维持当前会话的连贯性。 |
+| `session_id` | `str` | 否 | 会话 ID。作为“软信号”提升该会话内相关记忆的召回权重。 |
+
+### 2.2 MemCube 读写控制
+| 参数名 | 类型 | 默认值 | 说明 |
+| :--- | :--- | :--- | :--- |
+| **`readable_cube_ids`** | `list` | - | **读:** 允许检索的记忆 Cube 列表(可跨个人库与公共库)。 |
+| **`writable_cube_ids`** | `list` | - | **写:** 对话完成后,自动生成的记忆应存入的目标 Cube 列表。 |
+| **`add_message_on_answer`** | `bool` | `true` | 是否开启自动回写。建议开启以维持记忆的持续更新。 |
+
+### 2.3 算法与模型配置
+| 参数名 | 类型 | 默认值 | 说明 |
+| :--- | :--- | :--- | :--- |
+| `mode` | `str` | `fast` | 检索模式:`fast` (快速), `fine` (精细), `mixture` (混合)。 |
+| `model_name_or_path` | `str` | - | 指定使用的 LLM 模型名称或路径。 |
+| `system_prompt` | `str` | - | 覆盖默认的系统提示词。 |
+| `temperature` | `float` | - | 采样温度,控制生成文本的创造性。 |
+| `threshold` | `float` | `0.5` | 记忆召回的相关性阈值,低于该值的记忆将被剔除。 |
+
+## 3. 工作原理
+
+MemOS提供两种响应模式可供选型:
+### 3.1 全量响应 (`/complete`)
+* **特点**:等待模型生成全部内容后一次性返回 JSON。
+* **场景**:非交互式任务、后台逻辑处理、或对实时性要求较低的简单应用。
+
+### 3.2 流式响应 (`/stream`)
+* **特点**:采用 **Server-Sent Events (SSE)** 协议,实时推送 Token。
+* **场景**:聊天机器人、智能助手等需要即时打字机反馈效果的 UI 交互。
+
+## 4. 快速上手
+
+推荐使用开源版内置的 `MemOSClient` 进行调用。以下示例展示了如何询问关于 R 语言学习的建议,并利用记忆功能:
+
+```python
+from memos.api.client import MemOSClient
+
+client = MemOSClient(api_key="...", base_url="...")
+
+# 发起对话请求
+res = client.chat(
+ user_id="dev_user_01",
+ query="根据我之前的偏好,推荐一套 R 语言数据清理方案",
+ readable_cube_ids=["private_cube_01", "public_kb_r_lang"], # 读:个人偏好+公共库
+ writable_cube_ids=["private_cube_01"], # 写:沉淀至个人空间
+ add_message_on_answer=True, # 开启自动记忆回写
+ mode="fine" # 使用精细检索模式
+)
+
+if res:
+ print(f"AI 回复内容: {res.data}")
+```
+
+
+:::note
+**开发者提示:**
+若需要针对 `Playground` 环境进行调试,请访问专用的调试流接口 /product/chat/stream/playground 。
+:::
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/content/cn/open_source/open_source_api/core/add_memory.md b/content/cn/open_source/open_source_api/core/add_memory.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..8c446400
--- /dev/null
+++ b/content/cn/open_source/open_source_api/core/add_memory.md
@@ -0,0 +1,71 @@
+---
+title: 添加记忆 (Add Memory)
+desc: MemOS 的核心生产接口。通过 MemCube 隔离机制,实现个人记忆、知识库及多租户场景下的异步记忆生产。
+---
+
+**接口路径**:`POST /product/add`
+**功能描述**:这是系统存储非结构化数据的核心入口。它支持通过对话列表、纯文本或元数据,将原始数据转化为结构化的记忆片段。在开源版中,系统通过 **MemCube** 实现记忆的物理隔离与动态组织。
+
+## 1. 核心机理:MemCube 与隔离
+
+在开源架构中,理解 MemCube 是高效使用接口的关键:
+
+* **隔离单元**:MemCube 是记忆生成的原子单位,Cube 之间完全独立,系统仅在单个 Cube 内部进行去重和冲突解决。
+* **灵活映射**:
+ * **个人模式**:将 `user_id` 作为 `writable_cube_ids` 传入,即建立个人私有记忆。
+ * **知识库模式**:将知识库的唯一标识(QID)作为 `writable_cube_ids` 传入,内容即存入该知识库。
+* **多目标写入**:接口支持同时向多个 Cube 写入记忆,实现跨域同步。
+
+
+## 2. 关键接口参数
+
+核心参数定义如下:
+
+| 参数名 | 类型 | 必填 | 默认值 | 说明 |
+| :--- | :--- | :--- | :--- | :--- |
+| **`user_id`** | `str` | 是 | - | 用户唯一标识符,用于权限校验。 |
+| **`messages`** | `list/str`| 是 | - | 待存储的消息列表或纯文本内容。 |
+| **`writable_cube_ids`** | `list[str]`| 是 | - | **核心参数**:指定写入的目标 Cube ID 列表。 |
+| **`async_mode`** | `str` | 否 | `async` | 处理模式:`async` (后台队列处理) 或 `sync` (当前请求阻塞)。 |
+| **`is_feedback`** | `bool` | 否 | `false` | 若为 `true`,系统将自动路由至反馈处理器执行记忆更正。 |
+| `session_id` | `str` | 否 | `default` | 会话标识符,用于追踪对话上下文。 |
+| `custom_tags` | `list[str]`| 否 | - | 自定义标签,可作为后续搜索时的过滤条件。 |
+| `info` | `dict` | 否 | - | 扩展元数据。其中的所有键值对均支持后续过滤检索。 |
+| `mode` | `str` | 否 | - | 仅在 `async_mode='sync'` 时生效,可选 `fast` (快速) 或 `fine` (精细)。 |
+
+## 3. 工作原理 (Component & Handler)
+
+当请求到达后端时,系统由 **AddHandler** 调度核心组件执行以下逻辑:
+
+1. **多模态解析**:由 `MemReader` 组件将 `messages` 转化为内部记忆对象。
+2. **反馈路由**:若 `is_feedback=True`,Handler 会提取对话末尾作为反馈,直接修正已有记忆,不生成新事实。
+3. **异步分发**:若为 `async` 模式,`MemScheduler` 将任务推入任务队列,接口立即返回 `task_id`。
+4. **内部组织**:算法在目标 Cube 内执行组织逻辑,通过去重和融合优化记忆质量。
+
+## 4. 快速上手示例
+
+推荐使用 `MemOSClient` SDK 进行标准化调用:
+
+```python
+from memos.api.client import MemOSClient
+
+# 初始化客户端
+client = MemOSClient(api_key="...", base_url="...")
+
+# 场景一:为个人用户添加记忆
+client.add_message(
+ user_id="sde_dev_01",
+ writable_cube_ids=["user_01_private"],
+ messages=[{"role": "user", "content": "我正在学习 R 语言的 ggplot2。"}],
+ async_mode="async",
+ custom_tags=["Programming", "R"]
+)
+# 场景二:往知识库导入内容并开启反馈
+client.add_message(
+ user_id="admin_01",
+ writable_cube_ids=["kb_finance_2026"],
+ messages="2026年财务审计流程已更新,请参考附件。",
+ is_feedback=True, # 标记为反馈以更正旧版流程
+ info={"source": "Internal_Portal"}
+)
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/content/cn/open_source/open_source_api/core/delete_memory.md b/content/cn/open_source/open_source_api/core/delete_memory.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..e24af068
--- /dev/null
+++ b/content/cn/open_source/open_source_api/core/delete_memory.md
@@ -0,0 +1,62 @@
+---
+title: 删除记忆 (Delete Memory)
+desc: 从指定的 MemCube 中永久移除记忆条目、关联文件或符合特定过滤条件的记忆集合。
+---
+
+**接口路径**:`POST /product/delete_memory`
+**功能描述**:本接口用于维护记忆库的准确性与合规性。当用户要求遗忘特定信息、数据过时或需要清理特定的上传文件时,可以通过此接口在向量数据库与图数据库中同步执行物理删除。
+
+## 1. 核心机理:Cube 级物理清理
+
+在开源版中,删除操作遵循严格的 **MemCube** 隔离逻辑:
+
+* **作用域限制**:通过 `writable_cube_ids` 参数,删除操作被严格锁定在指定的记忆体中,绝不会误删其他 Cube 的内容。
+* **多维删除**:支持按 **记忆 ID**(精确)、**文件 ID**(关联删除)以及 **Filter 过滤器**(条件逻辑)三种维度并发执行清理。
+* **原子性同步**:删除操作由 **MemoryHandler** 触发,确保底层向量索引与图数据库中的实体节点同步移除,防止召回“幻觉”。
+
+
+
+## 2. 关键接口参数
+核心参数定义如下:
+
+| 参数名 | 类型 | 必填 | 说明 |
+| :--- | :--- | :--- | :--- |
+| **`writable_cube_ids`** | `list[str]` | 是 | 指定执行删除操作的目标 Cube 列表。 |
+| **`memory_ids`** | `list[str]` | 否 | 待删除的记忆唯一标识符列表。 |
+| **`file_ids`** | `list[str]` | 否 | 待删除的原始文件标识符列表,将同步清理该文件产生的全部记忆。 |
+| **`filter`** | `object` | 否 | 逻辑过滤器。支持按标签、元信息或时间戳批量删除符合条件的记忆。 |
+
+## 3. 工作原理 (MemoryHandler)
+
+1. **权限与路由**:系统通过 `user_id` 校验操作权限,并将请求路由至 **MemoryHandler**。
+2. **定位存储**:根据 `writable_cube_ids` 定位底层的 **naive_mem_cube** 组件。
+3. **分发清理任务**:
+ * **按 ID 清理**:直接根据 UUID 在主数据库和向量库中执行记录抹除。
+ * **按 Filter 清理**:先检索出符合条件的记忆 ID 集合,再执行批量物理移除。
+4. **状态反馈**:操作完成后返回成功状态,相关内容将立即从 [**检索接口**](./search_memory.md) 的召回范围中消失。
+
+## 4. 快速上手示例
+
+使用 `MemOSClient` 执行不同维度的删除操作:
+
+```python
+# 初始化客户端
+client = MemOSClient(api_key="...", base_url="...")
+
+# 场景一:精确删除单条已知的错误记忆
+client.delete_memory(
+ writable_cube_ids=["user_01_private"],
+ memory_ids=["2f40be8f-736c-4a5f-aada-9489037769e0"]
+)
+
+# 场景二:批量清理某一特定标签下的所有过时记忆
+client.delete_memory(
+ writable_cube_ids=["kb_finance_2026"],
+ filter={"tags": {"contains": "deprecated_policy"}}
+)
+```
+## 5. 注意事项
+
+不可恢复性:删除操作是物理删除。一旦执行成功,该记忆将无法再通过检索接口召回。
+
+文件关联性:通过 `file_ids` 删除时,系统会自动溯源并清理该文件解析出的事实记忆和摘要。
diff --git a/content/cn/open_source/open_source_api/core/get_memory.md b/content/cn/open_source/open_source_api/core/get_memory.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..d4353ae1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/content/cn/open_source/open_source_api/core/get_memory.md
@@ -0,0 +1,81 @@
+---
+title: 获取记忆 (Get Memories)
+desc: 分页查询或全量导出指定 Cube 中的记忆集合,支持按类型过滤及子图提取。
+---
+
+**接口路径**:
+* **分页查询**:`POST /product/get_memory`
+* **全量导出**:`POST /product/get_all`
+
+**功能描述**:用于列出或导出指定 **MemCube** 中的记忆资产。通过这两个接口,您可以获取系统生成的原始记忆片段、用户偏好或工具使用记录,支持分页展示与结构化导出。
+
+## 1. 核心机理:分页 vs. 全量导出
+
+在开源版中,系统通过 **MemoryHandler** 提供了两种不同的集合访问模式:
+
+* **业务分页模式 (`/get_memory`)**:
+ * **设计初衷**:为前端 UI 列表设计。支持 `page` 和 `page_size` 参数。
+ * **特性**:默认包含偏好记忆(`include_preference`),支持轻量级的数据加载。
+* **全量导出模式 (`/get_all`)**:
+ * **设计初衷**:为数据迁移或复杂关系分析设计。
+ * **核心能力**:支持传入 `search_query` 提取相关的**子图(Subgraph)**,或按 `memory_type`(文本/动作/参数)导出全量数据。
+
+
+## 2. 关键接口参数
+
+### 2.1 分页查询参数 (`/get_memory`)
+
+| 参数名 | 类型 | 必填 | 说明 |
+| :--- | :--- | :--- | :--- |
+| **`mem_cube_id`** | `str` | 是 | 目标 MemCube ID。 |
+| **`user_id`** | `str` | 否 | 用户唯一标识符。 |
+| **`page`** | `int` | 否 | 页码(从 1 开始)。若设为 `None` 则尝试全量导出。 |
+| **`page_size`** | `int` | 否 | 每页条目数。 |
+| `include_preference` | `bool` | 否 | 是否包含偏好记忆。 |
+
+### 2.2 全量/子图导出参数 (`/get_all`)
+
+| 参数名 | 类型 | 必填 | 说明 |
+| :--- | :--- | :--- | :--- |
+| **`user_id`** | `str` | 是 | 用户 ID。 |
+| **`memory_type`** | `str` | 是 | 记忆类型:`text_mem`, `act_mem`, `para_mem`。 |
+| `mem_cube_ids` | `list` | 否 | 待导出的 Cube ID 列表。 |
+| `search_query` | `str` | 否 | 若提供,将基于此查询召回并返回相关的记忆子图。 |
+
+## 3. 快速上手示例
+
+### 3.1 前端分页展示 (SDK 调用)
+
+```python
+# 获取第一页,每页 10 条记忆
+res = client.get_memory(
+ user_id="sde_dev_01",
+ mem_cube_id="cube_research_01",
+ page=1,
+ page_size=10
+)
+
+for mem in res.data:
+ print(f"[{mem['type']}] {mem['memory_value']}")
+```
+### 3.2 导出特定的事实记忆子图
+```python
+# 提取与“R 语言”相关的全部事实记忆
+res = client.get_all(
+ user_id="sde_dev_01",
+ memory_type="text_mem",
+ search_query="R language visualization"
+)
+```
+
+## 4. 响应结构说明
+接口返回标准的业务响应,其中 data 包含记忆对象数组。每条记忆通常包含以下核心字段:
+
+`id`: 记忆唯一标识,用于执行 获取详情 或 删除 操作。
+
+`memory_value`: 经过算法加工后的记忆文本。
+
+`tags`: 关联的自定义标签。
+
+::note
+开发者提示: 如果您已知记忆 ID 并希望查看其完整的元数据(如 confidence 或 usage 记录),请使用`获取记忆详情`(Get_ memory_by_id)接口。 :::
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/content/cn/open_source/open_source_api/core/get_memory_by_id.md b/content/cn/open_source/open_source_api/core/get_memory_by_id.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..ba11f6a9
--- /dev/null
+++ b/content/cn/open_source/open_source_api/core/get_memory_by_id.md
@@ -0,0 +1,58 @@
+---
+title: 获取记忆详情 (Get Memory Detail)
+desc: 通过记忆唯一标识符 (ID) 获取单条记忆的完整元数据,包括置信度、背景信息及使用记录。
+---
+
+**接口路径**:`GET /product/get_memory/{memory_id}`
+**功能描述**:本接口允许开发者检索单条记忆的所有底层细节。与返回摘要信息的检索接口不同,此接口会暴露该记忆的生命周期数据(如向量同步状态、AI 提取背景等),是系统管理与故障排查的核心工具。
+
+## 1. 为什么需要获取详情?
+
+* **元数据透视**:查看 AI 在提取该条记忆时的 `confidence`和 `background`。
+* **生命周期检验**:确认该记忆的 `vector_sync`(向量同步)是否成功,以及其 `updated_at` 时间戳。
+* **使用追踪**:通过 `usage` 记录,追踪该记忆在哪些会话中被召回并辅助了生成。
+
+
+## 2. 关键接口参数
+
+该接口采用标准的 RESTful 路径参数形式:
+
+| 参数名 | 位置 | 类型 | 必填 | 说明 |
+| :--- | :--- | :--- | :--- | :--- |
+| **`memory_id`** | Path | `str` | 是 | 记忆的唯一标识符(UUID)。您可以从 [**获取记忆列表**](./get_memory_list.md) 或 [**检索**](./search_memory.md) 的结果中获得此 ID。 |
+
+## 3. 工作原理 (MemoryHandler)
+
+1. **直通查询**:由 **MemoryHandler** 直接绕过业务编排层,与底层核心组件 **naive_mem_cube** 交互。
+2. **数据补全**:系统会从持久化数据库中拉取完整的 `metadata` 字典并返回,不进行任何语义截断。
+
+## 4. 响应数据详解
+
+响应体中的 `data` 对象包含以下核心字段:
+
+| 字段名 | 说明 |
+| :--- | :--- |
+| **`id`** | 记忆唯一标识符。 |
+| **`memory`** | 记忆的文本内容,通常包含标注(如 `[user观点]`)。 |
+| **`metadata.confidence`** | AI 提取该记忆的置信度分数(0.0 - 1.0)。 |
+| **`metadata.type`** | 记忆分类,如 `fact` (事实) 或 `preference` (偏好)。 |
+| **`metadata.background`** | 详细描述 AI 为何提取该记忆及其上下文背景。 |
+| **`metadata.usage`** | 列表形式,记录该记忆被模型使用的历史时间与环境。 |
+| **`metadata.vector_sync`**| 向量数据库同步状态,通常为 `success`。 |
+
+## 5. 快速上手示例
+
+使用 SDK 发起详情查询:
+
+```python
+# 假设已知一条记忆的 ID
+mem_id = "2f40be8f-736c-4a5f-aada-9489037769e0"
+
+# 获取完整详情
+res = client.get_memory_by_id(memory_id=mem_id)
+
+if res and res.code == 200:
+ metadata = res.data.get('metadata', {})
+ print(f"记忆背景: {metadata.get('background')}")
+ print(f"同步状态: {metadata.get('vector_sync')}")
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/content/cn/open_source/open_source_api/core/search_memory.md b/content/cn/open_source/open_source_api/core/search_memory.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..245fddae
--- /dev/null
+++ b/content/cn/open_source/open_source_api/core/search_memory.md
@@ -0,0 +1,95 @@
+---
+title: 检索记忆 (Search Memory)
+desc: 基于 MemCube 隔离机理,利用语义检索和逻辑过滤从记忆库中召回最相关的上下文信息。
+---
+
+**接口路径**:`POST /product/search`
+**功能描述**:本接口是 MemOS 实现检索增强生成 (RAG) 的核心。它能够跨越多个隔离的 **MemCube** 进行语义匹配,自动召回相关的事实、用户偏好及工具调用记录。
+
+## 1. 核心机理:Readable Cubes
+
+与云服务的单一用户视角不同,开源版接口通过 **`readable_cube_ids`** 实现了极其灵活的检索范围控制:
+
+* **跨 Cube 检索**:您可以同时指定多个 Cube ID(如 `[用户私有Cube, 企业公共知识库Cube]`),算法会并行从这些隔离的记忆体中召回最相关内容。
+* **软信号权重**:通过传入 `session_id`,系统会在召回时优先考虑该会话内的内容。这仅作为提升相关性的“权重”,而非强制过滤。
+* **绝对隔离**:未包含在 `readable_cube_ids` 列表中的 Cube 内容在算法层是完全不可见的,确保了多租户环境下的数据安全性。
+
+
+
+## 2. 关键接口参数
+
+核心检索参数定义如下:
+
+### 检索基础
+| 参数名 | 类型 | 必填 | 说明 |
+| :--- | :--- | :--- | :--- |
+| **`query`** | `str` | 是 | 用户的搜索查询语句,系统将基于此进行语义匹配。 |
+| **`user_id`** | `str` | 是 | 请求发起者的唯一标识,用于鉴权与上下文追踪。 |
+| **`readable_cube_ids`**| `list[str]`| 是 | **核心参数**:指定本次检索可读取的 Cube ID 列表。 |
+| **`mode`** | `str` | 否 | **搜索策略**:可选 `fast` (快速), `fine` (精细), `mixture` (混合)。 |
+
+### 召回控制
+| 参数名 | 类型 | 默认值 | 说明 |
+| :--- | :--- | :--- | :--- |
+| **`top_k`** | `int` | `10` | 召回文本记忆的数量上限。 |
+| **`include_preference`**| `bool` | `true` | 是否召回相关的用户偏好记忆(显式/隐式偏好)。 |
+| **`search_tool_memory`**| `bool` | `true` | 是否召回相关的工具调用记录。 |
+| **`filter`** | `dict` | - | 逻辑过滤器,支持按标签或元数据进行精确过滤。 |
+| **`dedup`** | `str` | - | 去重策略:`no` (不去重), `sim` (语义去重), `None` (默认精确文本去重)。 |
+
+## 3. 工作原理 (SearchHandler 策略)
+
+当请求到达后端时,**SearchHandler** 会根据指定的 `mode` 调用不同的组件执行检索:
+
+1. **查询重写**:利用 LLM 对用户的 `query` 进行语义增强,提升匹配精度。
+2. **多模式匹配**:
+ * **Fast 模式**:通过向量索引进行快速召回,适用于对响应速度要求极高的场景。
+ * **Fine 模式**:增加重排序(Rerank)环节,提升召回内容的相关度。
+ * **Mixture 模式**:结合语义搜索与图谱搜索,召回更具深度的关联记忆。
+3. **多维聚合**:系统并行检索事实、偏好(`pref_top_k`)和工具记忆(`tool_mem_top_k`),并将结果聚合返回。
+4. **后处理去重**:根据 `dedup` 配置对高度相似的记忆条目进行压缩。
+
+## 4. 快速上手示例
+
+通过 SDK 进行多 Cube 联合检索:
+
+```python
+from memos.api.client import MemOSClient
+
+client = MemOSClient(api_key="...", base_url="...")
+
+# 场景:同时检索用户记忆和两个专业知识库
+res = client.search_memory(
+ user_id="sde_dev_01",
+ query="根据我之前的偏好,推荐一些 R 语言的可视化方案",
+ # 传入可读的 Cube 列表,包括个人空间和两个知识库
+ readable_cube_ids=["user_01_private", "kb_r_lang", "kb_data_viz"],
+ mode="fine", # 使用精细模式以获得更准确的推荐
+ include_preference=True, # 召回“用户喜欢简洁风格”等偏好
+ top_k=5
+)
+
+if res:
+ # 结果包含在 memory_detail_list 中
+ print(f"召回结果: {res.data}")
+```
+
+## 5.进阶:使用过滤器 (Filter)
+SearchHandler 支持复杂的过滤器,以满足更细粒度的业务需求:
+```python
+
+# 示例:仅搜索标签为 "Programming" 且创建于 2026 年之后的记忆
+search_filter = {
+ "and": [
+ {"tags": {"contains": "Programming"}},
+ {"created_at": {"gt": "2026-01-01"}}
+ ]
+}
+
+res = client.search_memory(
+ query="数据清洗逻辑",
+ user_id="sde_dev_01",
+ readable_cube_ids=["user_01_private"],
+ filter=search_filter
+)
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/content/cn/open_source/open_source_api/help/error_codes.md b/content/cn/open_source/open_source_api/help/error_codes.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..1aa94ca3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/content/cn/open_source/open_source_api/help/error_codes.md
@@ -0,0 +1,48 @@
+---
+title: 错误码
+---
+
+| 错误码 | 含义 | 推荐解决方法 |
+| :--- | :--- | :--- |
+| **参数错误** | | |
+| 40000 | 请求参数错误 | 检查参数名、类型及格式是否符合要求 |
+| 40001 | 请求数据不存在 | 检查资源 ID(如 memory_id)是否正确 |
+| 40002 | 必填参数不能为空 | 补充缺失的必填字段 |
+| 40003 | 参数为空 | 检查传入的列表或对象是否为空 |
+| 40006 | 不支持的类型 | 检查 type 字段取值 |
+| 40007 | 不支持的文件类型 | 仅上传允许的格式(.pdf, .docx, .doc, .txt) |
+| 40008 | Base64 内容非法 | 检查 Base64 字符串是否包含非法字符 |
+| 40009 | Base64 格式非法 | 检查 Base64 编码格式是否正确 |
+| 40010 | 用户 ID 过长 | user_id 长度不能超过 100 字符 |
+| 40011 | 会话 ID 过长 | conversation_id 长度不能超过 100 字符 |
+| 40020 | 项目 ID 非法 | 确认 Project ID 格式正确 |
+| **认证与权限错误** | | |
+| 40100 | 需要 API Key 认证 | 在 Header 中添加有效 API Key |
+| 40130 | 需要 API Key 认证 | 在 Header 中添加有效 API Key |
+| 40132 | API Key 无效或已过期 | 检查 API Key 状态或重新生成 |
+| **配额与限流错误** | | |
+| 40300 | 超过接口调用次数上限 | 获取更多额度 |
+| 40301 | 超过请求 Token 调用上限 | 减少输入内容或获取更多额度 |
+| 40302 | 超过响应 Token 调用上限 | 缩短预期输出或获取更多额度 |
+| 40303 | 单次对话长度超过限制 | 缩减单次输入/输出长度 |
+| 40304 | 账户总 API 调用次数耗尽 | 获取更多额度 |
+| 40305 | 输入超过单次 Token 上限 | 缩减输入内容 |
+| 40306 | 删除记忆鉴权失败 | 确认是否有权删除该记忆 |
+| 40307 | 删除记忆不存在 | 检查 memory_id 是否有效 |
+| 40308 | 删除记忆对应的用户不存在 | 检查 user_id 是否正确 |
+| **系统与服务错误** | | |
+| 50000 | 系统内部异常 | 服务器繁忙或出现异常,请联系支持 |
+| 50002 | 操作失败 | 检查操作逻辑或稍后重试 |
+| 50004 | 记忆服务暂时不可用 | 稍后重试记忆写入/获取操作 |
+| 50005 | 搜索服务暂时不可用 | 稍后重试记忆搜索操作 |
+| **知识库与操作错误** | | |
+| 50103 | 文件数量超过限制 | 单次上传文件数量不超过20个 |
+| 50104 | 单个文件大小超过限制 | 确保单个文件不超过 100MB |
+| 50105 | 所有文件总大小超过限制 | 确保单次上传总大小不超过 300MB |
+| 50107 | 文件上传格式不符合要求 | 检查并更换文件格式 |
+| 50120 | 知识库不存在 | 确认知识库 ID 是否正确 |
+| 50123 | 知识库不关联此项目 | 确认知识库是否已授权给当前项目 |
+| 50131 | 任务不存在 | 检查 task_id 是否正确(常见于查询处理状态) |
+| 50143 | 添加记忆失败 | 算法服务处理异常,请稍后重试 |
+| 50144 | 添加消息失败 | 保存聊天历史记录失败 |
+| 50145 | 保存反馈并写入记忆失败 | 反馈处理过程中出现异常 |
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/content/cn/open_source/open_source_api/message/feedback.md b/content/cn/open_source/open_source_api/message/feedback.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..49cdd4de
--- /dev/null
+++ b/content/cn/open_source/open_source_api/message/feedback.md
@@ -0,0 +1,78 @@
+---
+title: 添加反馈
+desc: 提交用户对大模型回复的反馈内容,帮助 MemOS 实时更正、优化或删除不准确的记忆。
+---
+
+
+**接口路径**:`POST /product/feedback`
+**功能描述**:本接口用于处理用户对 AI 回复或记忆内容的反馈。通过分析 `feedback_content`,系统可以自动定位并修改存储在 **MemCube** 中的错误事实,或根据用户的正负反馈调整记忆的权重。
+
+## 1. 核心机理:记忆纠偏循环
+
+**FeedbackHandler** 提供了比普通添加接口更精细的控制逻辑:
+
+* **精确修正 (Precise Correction)**:通过提供 `retrieved_memory_ids`,系统可以直接针对某几条特定的检索结果进行更正,避免误伤其他记忆。
+* **语境分析**:结合 `history`(对话历史),系统能够理解反馈背后的真实意图(例如“你说错了,我现在的公司是 A 而不是 B”)。
+* **结果回显**:如果开启 `corrected_answer=true`,接口在处理完记忆更正后,会尝试返回一个基于新事实生成的更正后回答。
+
+## 2. 关键接口参数
+本接口核心参数定义如下:
+
+| 参数名 | 类型 | 必填 | 默认值 | 说明 |
+| :--- | :--- | :--- | :--- | :--- |
+| **`user_id`** | `str` | 是 | - | 用户唯一标识符。 |
+| **`history`** | `list` | 是 | - | 最近的对话历史,用于提供反馈的语境。 |
+| **`feedback_content`** | `str` | 是 | - | **核心:** 用户的反馈文本内容。 |
+| **`writable_cube_ids`**| `list` | 否 | - | 需要执行记忆更正的目标 Cube 列表。 |
+| `retrieved_memory_ids` | `list` | 否 | - | 可选。上一次检索出的、需要被修正的特定记忆 ID 列表。 |
+| `async_mode` | `str` | 否 | `async` | 处理模式:`async` (后台处理) 或 `sync` (实时处理并等待)。 |
+| `corrected_answer` | `bool` | 否 | `false` | 是否需要系统在修正记忆后返回一个纠正后的新回答。 |
+| `info` | `dict` | 否 | - | 附加元数据。 |
+
+## 3. 工作原理
+
+1. **冲突检测**:`FeedbackHandler` 接收反馈后,会对比 `history` 与 `writable_cube_ids` 中现有的记忆事实。
+2. **定位与更新**:
+ * 若提供了 `retrieved_memory_ids`,则直接更新对应节点。
+ * 若未提供 ID,系统通过语义匹配找到最相关的过时记忆进行覆盖或标记为无效。
+3. **权重调整**:对于态度模糊的反馈,系统会调整特定记忆条目的 `confidence`(置信度)或可信度等级。
+4. **异步生产**:在 `async` 模式下,修正逻辑由 `MemScheduler` 异步执行,接口立即返回 `task_id`。
+
+## 4. 快速上手示例
+
+
+```python
+from memos.api.client import MemOSClient
+
+client = MemOSClient(api_key="...", base_url="...")
+
+# 场景:修正 AI 关于用户职业的错误记忆
+res = client.add_feedback(
+ user_id="dev_user_01",
+ feedback_content="我不再减肥了,现在不需要控制饮食。",
+ history=[
+ {"role": "assistant", "content": "您正在减肥中,近期是否控制了摄入食物的热量?"},
+ {"role": "user", "content": "我不再减肥了..."}
+ ],
+ writable_cube_ids=["private_cube_01"],
+ # 指定具体的错误记忆 ID,以实现精准打击
+ retrieved_memory_ids=["mem_id_old_job_123"],
+ corrected_answer=True # 要求 AI 重新根据新事实回复我
+)
+
+if res and res.code == 200:
+ print(f"修正进度: {res.message}")
+ if res.data:
+ print(f"更正后的回复: {res.data}")
+```
+
+
+## 5. 使用场景
+### 5.1 纠正 AI 的错误推断
+人工干预:在管理后台提供“纠错”按钮,当管理员发现 AI 提取的记忆条目有误时,调用此接口进行人工更正。
+### 5.2 更新过时的用户偏好
+用户即时纠偏:在对话 UI 中,如果用户说出类似“记错了”、“不是这样的”等话语,可以自动触发此接口,利用 is_feedback=True 实现记忆的实时净化。
+
+::note
+如果反馈涉及的是公共知识库,请确保当前用户拥有对该 Cube 的写入权限。
+::
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/content/cn/open_source/open_source_api/message/get_message.md b/content/cn/open_source/open_source_api/message/get_message.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..5cfaeceb
--- /dev/null
+++ b/content/cn/open_source/open_source_api/message/get_message.md
@@ -0,0 +1,75 @@
+---
+title: 获取消息
+desc: 获取指定会话中的用户与助手原始对话历史,用于构建聊天 UI 或提取原始语境。
+---
+
+::warning
+**[直接看 API文档 点这里哦](/api_docs/message/get_message)**
+
+
+
+**本文聚焦于开源项目的功能说明,详细接口字段及限制请点击上方文字链接查看**
+::
+
+**接口路径**:`POST /product/get/message`
+**功能描述**:该接口用于获取指定会话中用户与助手的原始对话记录。与返回摘要信息的“记忆”接口不同,此接口返回的是未经加工的原始文本,是构建聊天历史回溯功能的核心接口。
+
+## 1. 记忆 (Memory) vs 消息 (Message)
+
+在开发过程中,请区分以下两类数据:
+* **获取记忆 (`/get_memory`)**:返回的是系统处理后的**事实与偏好摘要**(例如:“用户喜欢 R 语言进行可视化”)。
+* **获取消息 (`/get_message`)**:返回的是**原始对话文本**(例如:“我最近在自学 R 语言,推荐个可视化包”)。
+
+## 2. 关键接口参数
+本接口支持以下参数:
+
+| 参数名 | 类型 | 必填 | 默认值 | 说明 |
+| :--- | :--- | :--- | :--- | :--- |
+| `user_id` | `str` | 是 | - | 与获取消息关联的用户唯一标识符。 |
+| `conversation_id` | `str` | 否 | `None` | 指定会话的唯一标识符。 |
+| `message_limit_number` | `int` | 否 | `6` | 限制返回的消息条数,最大建议值为 50。 |
+| `conversation_limit_number`| `int` | 否 | `6` | 限制返回的会话历史条数。 |
+| `source` | `str` | 否 | `None` | 标识消息的来源渠道。 |
+
+## 3. 工作原理
+
+
+1. **定位会话**:系统根据提供的 `conversation_id` 在底层存储中检索属于该用户及会话的消息记录。
+2. **切片处理**:根据 `message_limit_number` 参数,系统从最新的消息开始倒序截取指定条数,确保返回的是最近的对话。
+3. **安全隔离**:所有请求均通过 `RequestContextMiddleware` 中间件,严格校验 `user_id` 的归属权,防止越权访问。
+
+## 4. 快速上手示例
+
+使用开源版内置的 `MemOSClient` 快速拉取对话历史:
+
+```python
+from memos.api.client import MemOSClient
+
+# 初始化客户端
+client = MemOSClient(
+ api_key="YOUR_LOCAL_API_KEY",
+ base_url="http://localhost:8000/product"
+)
+
+# 获取指定会话的最近 10 条对话记录
+res = client.get_message(
+ user_id="memos_user_123",
+ conversation_id="conv_r_study_001",
+ message_limit_number=10
+)
+
+if res and res.code == 200:
+ # 遍历返回的消息列表
+ for msg in res.data:
+ print(f"[{msg['role']}]: {msg['content']}")
+```
+
+## 5. 使用场景
+### 5.1 聊天 UI 历史加载
+当用户点击进入某个历史会话时,调用此接口可恢复对话现场。建议结合 `message_limit_number` 实现分页加载,提升前端性能。
+
+### 5.2 外部模型上下文注入
+如果您正在使用自定义的大模型逻辑(非 MemOS 内置 chat 接口),可以通过此接口获取原始对话历史,并将其手动拼接至模型的 messages 数组中。
+
+### 5.3 消息回溯分析
+您可以定期导出原始对话记录,用于评估 AI 的回复质量或分析用户的潜在意图。
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/content/cn/open_source/open_source_api/message/get_suggestion_queries.md b/content/cn/open_source/open_source_api/message/get_suggestion_queries.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..76ab87bd
--- /dev/null
+++ b/content/cn/open_source/open_source_api/message/get_suggestion_queries.md
@@ -0,0 +1,70 @@
+---
+title: 获取建议问题 (Get Suggestions)
+desc: 基于当前对话语境或 Cube 内的近期记忆,自动生成 3 条后续对话建议。
+---
+
+# 获取建议问题 (Get Suggestion Queries)
+
+**接口路径**:`POST /product/suggestions`
+**功能描述**:本接口用于实现“猜你想问”功能。系统会根据提供的对话上下文或目标 **MemCube** 中的近期记忆,通过大语言模型生成 3 个相关的建议问题,帮助用户延续对话。
+
+## 1. 核心机理:双模式生成策略
+
+**SuggestionHandler** 根据入参的不同,支持两种灵活的生成模式:
+
+* **基于对话的即时建议 (Context-based)**:
+ * **触发条件**:在请求中提供了 `message`(对话记录)。
+ * **逻辑**:系统分析最近的对话内容,生成 3 个与当前话题紧密相关的后续问题。
+* **基于记忆的发现建议 (Memory-based)**:
+ * **触发条件**:未提供 `message`。
+ * **逻辑**:系统会从 `mem_cube_id` 指定的记忆体中检索“最近记忆”,并据此生成与用户近期生活、工作状态相关的启发式问题。
+
+
+
+## 2. 关键接口参数
+
+核心参数定义如下:
+
+| 参数名 | 类型 | 必填 | 默认值 | 说明 |
+| :--- | :--- | :--- | :--- | :--- |
+| **`user_id`** | `str` | 是 | - | 用户唯一标识符。 |
+| **`mem_cube_id`** | `str` | 是 | - | **核心参数**:指定建议生成所依据的记忆空间。 |
+| **`language`** | `str` | 否 | `zh` | 生成建议使用的语言:`zh` (中文) 或 `en` (英文)。 |
+| `message` | `list/str`| 否 | - | 当前对话上下文。若提供,则生成基于对话的建议。 |
+
+## 3. 工作原理 (SuggestionHandler)
+
+1. **语境识别**:`SuggestionHandler` 首先检查 `message` 字段。若有值,则提取对话精髓;若为空,则转向底层 `MemCube` 获取最近动态。
+2. **模板匹配**:系统根据 `language` 参数自动切换内置的中英文提示词模板(Prompt Templates)。
+3. **模型推理**:调用 LLM 对背景资料进行推导,确保生成的 3 个问题既符合逻辑又具有启发性。
+4. **格式化输出**:将建议问题以数组形式返回,便于前端直接渲染为点击按钮。
+
+## 4. 快速上手示例
+
+使用 SDK 获取针对当前对话的中文建议:
+
+```python
+from memos.api.client import MemOSClient
+
+client = MemOSClient(api_key="...", base_url="...")
+
+# 场景:根据刚刚关于“R语言”的对话生成建议
+res = client.get_suggestions(
+ user_id="dev_user_01",
+ mem_cube_id="private_cube_01",
+ language="zh",
+ message=[
+ {"role": "user", "content": "我想学习 R 语言的可视化。"},
+ {"role": "assistant", "content": "推荐您学习 ggplot2 包,它是 R 语言可视化的核心工具。"}
+ ]
+)
+
+if res and res.code == 200:
+ # 示例输出: ["如何安装 ggplot2?", "有哪些经典的 ggplot2 教程?", "R 语言还有哪些可视化包?"]
+ print(f"建议问题: {res.data}")
+```
+
+## 5. 使用场景建议
+对话引导:在 AI 回复完用户后,自动调用此接口,在回复框下方展示建议按钮,引导用户深入探讨。
+
+冷启动激活:当用户进入一个新的会话且尚未发言时,通过“基于记忆模式”展示用户可能感兴趣的往期话题,打破沉默。
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/content/cn/open_source/open_source_api/scheduler/ wait.md b/content/cn/open_source/open_source_api/scheduler/ wait.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..e1ddcef7
--- /dev/null
+++ b/content/cn/open_source/open_source_api/scheduler/ wait.md
@@ -0,0 +1,77 @@
+---
+title: 高级任务同步 (Advanced Task Synchronization)
+desc: 提供阻塞等待与流式进度观测能力,确保在执行后续操作前,指定用户的异步任务已全部处理完成。
+---
+
+
+**接口路径**:
+* **同步阻塞等待**:`POST /product/scheduler/wait`
+* **实时进度流 (SSE)**:`GET /product/scheduler/wait/stream`
+
+**功能描述**:在自动化脚本、数据迁移或集成测试场景中,通常需要确保所有的异步记忆提取任务(如 LLM 事实提取、向量入库)已完全结束。本模块接口允许客户端“挂起”请求,直到调度器检测到目标用户的任务队列已清空。
+
+## 1. 核心机理:调度器空闲检测
+
+系统通过 **SchedulerHandler** 实时监控底层 **MemScheduler** 的运行状态:
+
+* **队列检查**:系统会检查 Redis Stream 中属于该用户的待处理任务(Pending)及排队任务(Remaining)。
+* **空闲判定**:仅当队列计数为 0 且当前没有 Worker 正在执行该用户的任务时,判定为“空闲 (Idle)”。
+* **超时保护**:为防止无限期阻塞,接口支持设置 `timeout_seconds`。若达到上限任务仍未完成,接口将返回当前状态并停止等待。
+
+
+
+## 2. 关键接口参数
+
+这两个接口共享以下查询参数(Query Parameters):
+
+| 参数名 | 类型 | 必填 | 默认值 | 说明 |
+| :--- | :--- | :--- | :--- | :--- |
+| **`user_name`** | `str` | 是 | - | 目标用户的名称或 ID。 |
+| `timeout_seconds`| `num` | 否 | - | 最大等待时长(秒)。超过此时间将自动返回。 |
+| `poll_interval` | `num` | 否 | - | 内部检查队列状态的频率(秒)。 |
+
+## 3. 响应模式选型
+
+### 3.1 同步阻塞模式 (`/wait`)
+* **特点**:标准的 HTTP 响应。连接会保持开启,直到任务清空或超时。
+* **场景**:编写自动化测试脚本或在执行 `search` 前确保数据已入库。
+
+### 3.2 实时流模式 (`/wait/stream`)
+* **特点**:基于 **Server-Sent Events (SSE)** 技术。
+* **场景**:在管理后台展示动态进度条,实时显示任务队列的缩减过程。
+
+## 4. 快速上手示例
+
+使用开源版 SDK 进行阻塞式等待:
+
+```python
+from memos.api.client import MemOSClient
+
+client = MemOSClient(api_key="...", base_url="...")
+user_name = "dev_user_01"
+
+# --- 场景 A:同步阻塞等待 (常用于 Python 自动化脚本) ---
+print(f"正在等待用户 {user_name} 的任务队列清空...")
+res = client.wait_until_idle(
+ user_name=user_name,
+ timeout_seconds=300,
+ poll_interval=2
+)
+if res and res.code == 200:
+ print("✅ 任务已全部完成。")
+
+# --- 场景 B:流式进度观测 (常用于前端进度条渲染) ---
+print("开始监听任务实时进度流...")
+# 注意:SSE 接口在 SDK 中通常返回一个生成器 (Generator)
+progress_stream = client.stream_scheduler_progress(
+ user_name=user_name,
+ timeout_seconds=300
+)
+
+for event in progress_stream:
+ # 实时打印剩余任务数
+ print(f"当前排队任务数: {event['remaining_tasks_count']}")
+ if event['status'] == 'idle':
+ print("🎉 调度器已空闲")
+ break
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/content/cn/open_source/open_source_api/scheduler/get_status.md b/content/cn/open_source/open_source_api/scheduler/get_status.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..624fa394
--- /dev/null
+++ b/content/cn/open_source/open_source_api/scheduler/get_status.md
@@ -0,0 +1,97 @@
+---
+title: 任务调度与状态监控 (Scheduler Status)
+desc: 监控 MemOS 异步任务的生命周期,提供包括任务进度、队列积压及系统负载在内的全方位观测能力。
+---
+
+**接口路径**:
+* **系统级概览**:`GET /product/scheduler/allstatus`
+* **任务进度查询**:`GET /product/scheduler/status`
+* **用户队列指标**:`GET /product/scheduler/task_queue_status`
+
+**功能描述**:本模块接口旨在为开发者提供异步记忆生产链路的可观测性。通过这些接口,您可以实时追踪特定任务的完成状态,监控 Redis 任务队列的积压情况,以及获取整个调度系统的运行指标。
+
+## 1. 核心机理:MemScheduler 调度体系
+
+在开源架构中,**MemScheduler** 负责处理所有高耗时的后台任务(如 LLM 记忆提取、向量索引构建等):
+
+* **状态流转**:任务在生命周期内会经历 `waiting` (等待中)、`in_progress` (执行中)、`completed` (已完成) 或 `failed` (失败) 等状态。
+* **队列监控**:系统基于 Redis Stream 实现任务分发。通过监控 `pending` (已交付未确认) 和 `remaining` (排队中) 任务数,可以评估系统的处理压力。
+* **多维度观测**:支持从“单任务”、“单用户队列”以及“全系统 summary”三个维度进行状态透视。
+
+
+## 2. 接口详解
+
+### 2.1 任务进度查询 (`/status`)
+用于追踪特定异步任务的当前执行阶段。
+
+| 参数名 | 类型 | 必填 | 说明 |
+| :--- | :--- | :--- | :--- |
+| **`user_id`** | `str` | 是 | 请求查询的用户唯一标识符。 |
+| `task_id` | `str` | 否 | 可选。若提供,则仅查询该特定任务的状态。 |
+
+**返回状态说明**:
+* `waiting`: 任务已进入队列,等待空闲 Worker 执行。
+* `in_progress`: Worker 正在调用大模型提取记忆或写入数据库。
+* `completed`: 记忆已成功持久化并完成向量索引同步。
+* `failed`: 任务失败。
+
+### 2.2 用户队列指标 (`/task_queue_status`)
+用于监控指定用户在 Redis 中的任务积压情况。
+
+| 参数名 | 类型 | 必填 | 说明 |
+| :--- | :--- | :--- | :--- |
+| **`user_id`** | `str` | 是 | 需查询队列状况的用户 ID。 |
+
+**核心指标项**:
+* `pending_tasks_count`: 已分发给 Worker 但尚未收到确认(Ack)的任务数。
+* `remaining_tasks_count`: 当前仍在队列中排队等待分配的任务总数。
+* `stream_keys`: 匹配到的 Redis Stream 键名列表。
+
+### 2.3 系统级概览 (`/allstatus`)
+获取调度器的全局运行概况,通常用于管理员后台监控。
+
+* **核心返回信息**:
+ * `scheduler_summary`: 包含系统当前的负载与健康状况。
+ * `all_tasks_summary`: 所有正在运行及排队任务的聚合统计。
+
+## 3. 工作原理 (SchedulerHandler)
+
+当您发起状态查询请求时,**SchedulerHandler** 会执行以下操作:
+
+1. **缓存检索**:首先从 Redis 状态缓存中查找 `task_id` 对应的实时进度。
+2. **队列确认**:若查询队列指标,Handler 会调用 Redis 统计指令(如 `XLEN`, `XPENDING`)分析 Stream 状态。
+3. **指标聚合**:对于全局状态请求,Handler 会汇总所有活跃节点的指标,生成系统级的 summary 数据。
+
+## 4. 快速上手示例
+
+使用 SDK 轮询任务状态直至完成:
+
+```python
+from memos.api.client import MemOSClient
+import time
+
+client = MemOSClient(api_key="...", base_url="...")
+
+# 1. 系统级概览:查看整个 MemOS 系统的运行健康度
+global_res = client.get_all_scheduler_status()
+if global_res:
+ print(f"系统运行概况: {global_res.data['scheduler_summary']}")
+
+# 2. 队列指标监控:检查特定用户的任务积压情况
+queue_res = client.get_task_queue_status(user_id="dev_user_01")
+if queue_res:
+ print(f"待处理任务数: {queue_res.data['remaining_tasks_count']}")
+ print(f"已下发未完成任务数: {queue_res.data['pending_tasks_count']}")
+
+# 3. 任务进度追踪:轮询特定任务直至结束
+task_id = "task_888999"
+while True:
+ res = client.get_task_status(user_id="dev_user_01", task_id=task_id)
+ if res and res.code == 200:
+ current_status = res.data[0]['status'] # data 为状态列表
+ print(f"任务 {task_id} 当前状态: {current_status}")
+
+ if current_status in ['completed', 'failed', 'cancelled']:
+ break
+ time.sleep(2)
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/content/cn/open_source/open_source_api/start/configuration.md b/content/cn/open_source/open_source_api/start/configuration.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..271d3ded
--- /dev/null
+++ b/content/cn/open_source/open_source_api/start/configuration.md
@@ -0,0 +1,7 @@
+---
+title: 项目配置
+---
+
+关于 MemOS 开源版 API 服务器的详细配置说明(包括 LLM 引擎、存储后端及环境变量设置),请参考:
+
+👉 [**REST API 服务器配置指南**](../../../getting_started/rest_api_server.md)
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/content/cn/open_source/open_source_api/start/overview.md b/content/cn/open_source/open_source_api/start/overview.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..4804772b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/content/cn/open_source/open_source_api/start/overview.md
@@ -0,0 +1,52 @@
+---
+title: 概述
+---
+
+## 1. 接口介绍
+
+MemOS 开源项目提供了一套基于 **FastAPI** 编写的高性能 REST API 服务。系统采用 **Component (组件) + Handler (处理器)** 架构,所有核心逻辑(如记忆提取、语义搜索、异步调度)均可通过标准的 REST 接口进行调用。
+
+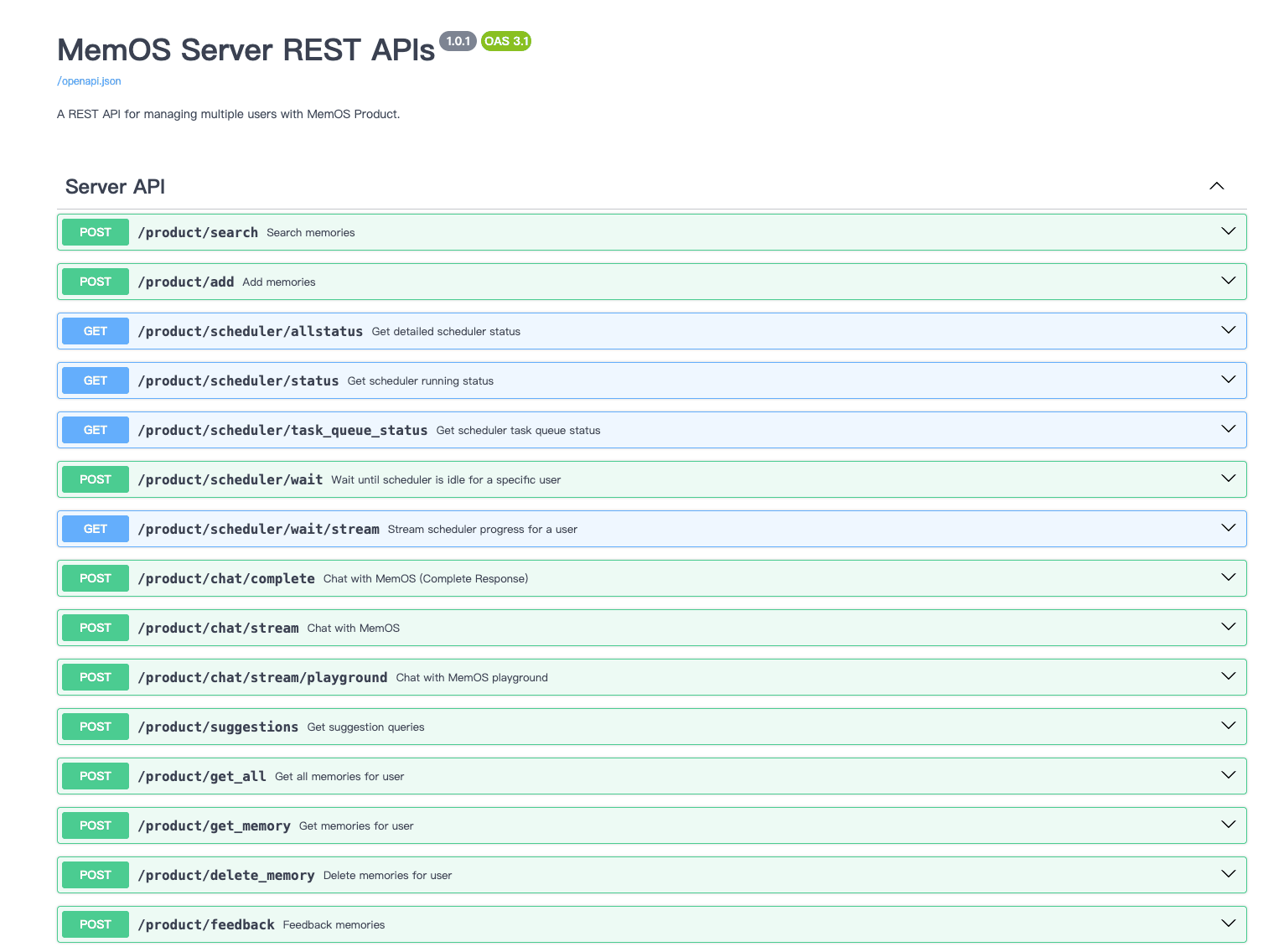
+MemOS REST API 服务架构概览
+
+### 核心功能特点
+
+* **多维记忆生产**:支持通过 `AddHandler` 处理对话、文本或文档,并自动转化为结构化记忆。
+* **MemCube 物理隔离**:基于 Cube ID 实现不同用户或知识库之间的数据物理隔离与独立索引。
+* **端到端对话闭环**:通过 `ChatHandler` 编排“检索 -> 生成 -> 异步存储”的全流程。
+* **异步任务调度**:内置 `MemScheduler` 调度引擎,支持大规模记忆生产任务的削峰填谷与状态追踪。
+* **自我纠偏机制**:提供反馈接口,允许利用自然语言对已存储的记忆进行修正或标记。
+
+## 2. 入门指南
+
+通过以下两个核心步骤,快速将记忆能力集成到您的 AI 应用中:
+
+* [**添加记忆**](./core/add_memory.md):通过 `POST /product/add` 接口,将原始消息流写入指定的 MemCube,开启生产链路。
+* [**检索记忆**](./core/search_memory.md):通过 `POST /product/search` 接口,基于语义相似度从多个 Cube 中召回相关上下文。
+
+## 3. 接口分类
+
+MemOS 的功能接口分为以下几大类:
+
+* **[核心记忆 (Core)](./core/add_memory.md)**:包含记忆的增、删、改、查等原子操作。
+* **[智能对话 (Chat)](./chat/chat.md)**:实现带记忆增强的流式或全量对话响应。
+* **[消息管理 (Message)](./message/feedback.md)**:涵盖用户反馈、猜你想问(Suggestion)等增强交互接口。
+* **[异步调度 (Scheduler)](./scheduler/get_status.md)**:用于监控后台记忆提取任务的进度与队列状态。
+* **[系统工具 (Tools)](./tools/check_cube.md)**:提供 Cube 存在性校验及记忆归属反查等辅助功能。
+
+## 4. 鉴权认证与上下文
+
+### 鉴权机制
+在开源环境中,所有的 API 请求需要在 Header 中包含 `Authorization` 字段。
+* **开发环境**:您可以在本地 `.env` 或 `configuration.md` 中自定义 `API_KEY`。
+* **生产部署**:建议通过 `RequestContextMiddleware` 扩展 OAuth2 或更高级的身份校验逻辑。
+
+### 请求上下文
+* **user_id**:请求体中必须包含此标识,用于 Handler 层的身份追踪。
+* **MemCube ID**:开源版的核心隔离单元。通过指定 `readable_cube_ids` 或 `writable_cube_ids`,您可以精确控制数据读写的物理边界。
+
+## 5. 下一步行动
+
+* 👉 [**系统配置**](./start/configuration.md):配置您的 LLM 提供商与向量数据库引擎。
+* 👉 [**添加第一条记忆**](./core/add_memory.md):尝试通过 SDK 或 Curl 提交第一组对话消息。
+* 👉 [**探索常见错误**](./help/error_codes.md):了解 API 状态码及其背后的异常处理机制。
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/content/cn/open_source/open_source_api/tools/check_cube.md b/content/cn/open_source/open_source_api/tools/check_cube.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..37029e70
--- /dev/null
+++ b/content/cn/open_source/open_source_api/tools/check_cube.md
@@ -0,0 +1,50 @@
+---
+title: 检查 MemCube 存在性 (Check Cube Existence)
+desc: 校验指定的 MemCube ID 是否已在系统中初始化并可用。
+---
+
+**接口路径**:`POST /product/exist_mem_cube_id`
+**功能描述**:本接口用于验证指定的 `mem_cube_id` 是否已经存在于系统中。它是确保数据一致性的“守门员”接口,建议在动态创建知识库或为新用户分配空间前调用,以避免重复初始化或无效操作。
+
+## 1. 核心机理:Cube 索引校验
+
+在 MemOS 架构中,MemCube 的存在性决定了后续所有记忆操作的合法性:
+
+* **逻辑校验**:系统通过 **MemoryHandler** 检索底层存储索引,确认该 ID 是否已注册。
+* **冷启动保障**:对于按需创建 Cube 的场景,该接口可用于判断是否需要执行初次 `add` 操作来激活记忆空间。
+
+
+
+## 2. 关键接口参数
+请求体定义如下:
+
+| 参数名 | 类型 | 必填 | 说明 |
+| :--- | :--- | :--- | :--- |
+| **`mem_cube_id`** | `str` | 是 | 待校验的 MemCube 唯一标识符。 |
+
+## 3. 工作原理 (MemoryHandler)
+
+1. **直通索引**:**MemoryHandler** 接收请求后,直接调用底层 **naive_mem_cube** 的元数据查询接口。
+2. **状态检索**:系统在持久化层中查找该 ID 对应的配置文件或数据库记录。
+3. **布尔反馈**:返回结果不包含记忆内容,仅以 `code` 或 `data` 形式告知该 Cube 是否已激活。
+
+## 4. 快速上手示例
+
+使用 SDK 校验目标 Cube 状态:
+
+```python
+from memos.api.client import MemOSClient
+
+client = MemOSClient(api_key="...", base_url="...")
+
+# 场景:在导入文档前确认目标知识库已创建
+kb_id = "kb_finance_2026"
+res = client.exist_mem_cube_id(mem_cube_id=kb_id)
+
+if res and res.code == 200:
+ # 假设 data 字段返回布尔值或存在性对象
+ if res.data.get('exists'):
+ print(f"✅ MemCube '{kb_id}' 已就绪。")
+ else:
+ print(f"❌ MemCube '{kb_id}' 尚未初始化。")
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/content/cn/open_source/open_source_api/tools/get_user_names.md b/content/cn/open_source/open_source_api/tools/get_user_names.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..71073418
--- /dev/null
+++ b/content/cn/open_source/open_source_api/tools/get_user_names.md
@@ -0,0 +1,53 @@
+---
+title: 反向查询用户 (Get User Names)
+desc: 通过记忆唯一标识符 (ID) 反向查询该条记忆所属的用户名称。
+---
+
+**接口路径**:`POST /product/get_user_names_by_memory_ids`
+**功能描述**:本接口提供了一种“逆向追踪”能力。当您在系统日志或共享存储中获取到特定的 `memory_id`,但无法确定其产生者时,可以使用此接口批量获取对应的用户名。
+
+## 1. 核心机理:元数据溯源
+
+在 MemOS 的存储架构中,每条生成的记忆条目都与原始用户的元数据绑定。本接口通过以下逻辑执行溯源:
+
+* **多对一映射**:支持一次传入多个 `memory_id`,系统将返回对应的用户列表。
+* **管理透明度**:该工具通常用于管理后台,帮助管理员识别公共 Cube 中不同条目的贡献者。
+
+
+
+## 2. 关键接口参数
+
+请求体定义如下:
+
+| 参数名 | 类型 | 必填 | 说明 |
+| :--- | :--- | :--- | :--- |
+| **`memory_ids`** | `list[str]` | 是 | 待查询的记忆唯一标识符列表。 |
+
+## 3. 工作原理 (MemoryHandler)
+
+1. **ID 解析**:**MemoryHandler** 接收 ID 列表后,查询全局索引表。
+2. **关系检索**:系统从底层的持久化层(或关系图谱节点)中提取关联的 `user_id` 或 `user_name` 属性。
+3. **数据脱敏**:根据系统配置,返回对应的用户显示名称或标识符。
+
+## 4. 快速上手示例
+
+使用 SDK 执行反向查询:
+
+```python
+from memos.api.client import MemOSClient
+
+client = MemOSClient(api_key="...", base_url="...")
+
+# 准备待查的记忆 ID 列表
+target_ids = [
+ "2f40be8f-736c-4a5f-aada-9489037769e0",
+ "5e92be1a-826d-4f6e-97ce-98b699eebb98"
+]
+
+# 执行查询
+res = client.get_user_names_by_memory_ids(memory_ids=target_ids)
+
+if res and res.code == 200:
+ # res.data 通常返回一个映射字典或用户列表
+ print(f"该记忆片段归属于用户: {res.data}")
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/content/cn/settings.yml b/content/cn/settings.yml
index 674265d6..a65ce56d 100644
--- a/content/cn/settings.yml
+++ b/content/cn/settings.yml
@@ -42,19 +42,19 @@ nav:
- "(ri:lightbulb-line) 核心概念": open_source/home/core_concepts.md
- "(ri:building-2-line) 架构设计": open_source/home/architecture.md
- "(ri:file-code-line) REST API 服务": open_source/getting_started/rest_api_server.md
- - "(ri:code-line) 示例": open_source/getting_started/examples.md
+ - "(ri:code-line) MemOS示例": open_source/getting_started/examples.md
- "(ri:cpu-line) MemOS":
- - "(ri:eye-line) 概览": open_source/modules/mos/overview.md
- - "(ri:checkbox-multiple-blank-line) 记忆立方": open_source/modules/mem_cube.md
- - "(ri:book-open-line) 记忆读取": open_source/modules/mem_reader.md
- - "(ri:calendar-line) 记忆调度": open_source/modules/mem_scheduler.md
- - "(ri:calendar-line) 使用记忆进行聊天": open_source/modules/mem_chat.md
- - "(ri:feedback-line) 记忆修正": open_source/modules/mem_feedback.md
+ - "(ri:eye-line) API 开发指南": open_source/modules/mos/overview.md
+ - "(ri:checkbox-multiple-blank-line) MemCube记忆立方": open_source/modules/mem_cube.md
+ - "(ri:book-open-line) MemReader记忆读取": open_source/modules/mem_reader.md
+ - "(ri:calendar-line) MemScheduler记忆调度": open_source/modules/mem_scheduler.md
+ - "(ri:calendar-line) MemChat使用记忆进行聊天": open_source/modules/mem_chat.md
+ - "(ri:feedback-line) MemFeedback记忆反馈": open_source/modules/mem_feedback.md
- "(ri:brain-line) 记忆系统":
- - "(ri:database-2-line) 概览": open_source/modules/memories/overview.md
+ - "(ri:database-2-line) 记忆模块总览": open_source/modules/memories/overview.md
- "(ri:book-2-line) 明文记忆":
- "(ri:file-text-line) 简单明文记忆": open_source/modules/memories/naive_textual_memory.md
- "(ri:file-text-line) 通用明文记忆": open_source/modules/memories/general_textual_memory.md
@@ -72,12 +72,12 @@ nav:
- "(ri:tools-line) Coze空间配置Memos的MCP": open_source/best_practice/mcp_for_cozespace_and_tools.md
- "(ri:heart-line) 贡献指南":
- - "(ri:eye-line) 总览": open_source/contribution/overview.md
- - "(ri:tools-line) 环境配置": open_source/contribution/setting_up.md
+ - "(ri:eye-line) 参与 MemOS 开发": open_source/contribution/overview.md
+ - "(ri:tools-line) 配置开发环境": open_source/contribution/setting_up.md
- "(ri:git-branch-line) 开发流程": open_source/contribution/development_workflow.md
- "(ri:git-commit-line) 提交规范": open_source/contribution/commit_guidelines.md
- - "(ri:article-line) 文档编写": open_source/contribution/writing_docs.md
- - "(ri:flask-line) 测试编写": open_source/contribution/writing_tests.md
+ - "(ri:article-line) 文档编写指南": open_source/contribution/writing_docs.md
+ - "(ri:flask-line) 如何编写测试": open_source/contribution/writing_tests.md
- "(ri:file-code-line) API 参考文档": api-reference/search-memories
diff --git a/content/en/open_source/modules/mem_cube.md b/content/en/open_source/modules/mem_cube.md
index 12544356..89a53b7a 100644
--- a/content/en/open_source/modules/mem_cube.md
+++ b/content/en/open_source/modules/mem_cube.md
@@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
---
-title: MemCube Overview
+title: MemCube
desc: "`MemCube` is the core organizational unit in MemOS, designed to encapsulate and manage all types of memory for a user or agent. It provides a unified interface for loading, saving, and operating on multiple memory modules, making it easy to build, share, and deploy memory-augmented applications."
---
## What is a MemCube?
diff --git a/content/en/open_source/modules/memories/general_textual_memory.md b/content/en/open_source/modules/memories/general_textual_memory.md
index 97376bb5..a495a7d7 100644
--- a/content/en/open_source/modules/memories/general_textual_memory.md
+++ b/content/en/open_source/modules/memories/general_textual_memory.md
@@ -42,6 +42,20 @@ Each memory is represented as a `TextualMemoryItem`:
All values are validated. Invalid values will raise errors.
+### Search Mechanism
+Unlike NaiveTextMemory, which relies on keyword matching, GeneralTextMemory utilizes vector-based semantic search.
+
+## Algorithm Comparison
+
+| Feature | Keyword Matching | Vector Semantic Search |
+| ------------------ | ---------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------ |
+| **Semantic Understanding** | ❌ Doesn't understand synonyms | ✅ Understands similar concepts |
+| **Resource Usage** | ✅ Extremely low | ⚠️ Requires embedding model and vector DB |
+| **Execution Speed** | ✅ Fast (O(n)) | ⚠️ Slower (indexing + querying) |
+| **Suitable Scale** | < 1K memories | 10K - 100K memories |
+| **Predictability** | ✅ Intuitive results | ⚠️ Black box model
+
+
## API Summary (`GeneralTextMemory`)
### Initialization
@@ -112,13 +126,13 @@ m.dump("tmp/mem")
m.load("tmp/mem")
```
-::alert{type="info"}
+::note
**Extension: Internet Retrieval**
GeneralTextMemory can be combined with Internet Retrieval to extract content from web pages and add to memory.
View example: [Retrieve Memories from the Internet](./tree_textual_memory#retrieve-memories-from-the-internet-optional)
::
-::alert{type="info"}
+::note
**Advanced: Using MultiModal Reader**
For processing images, URLs, or files within conversations, see the comprehensive MultiModal Reader examples.
View documentation: [Using MultiModalStructMemReader](./tree_textual_memory#using-multimodalstructmemreader-advanced)
diff --git a/content/en/open_source/modules/memories/naive_textual_memory.md b/content/en/open_source/modules/memories/naive_textual_memory.md
index 81fa9fdf..6993f7a7 100644
--- a/content/en/open_source/modules/memories/naive_textual_memory.md
+++ b/content/en/open_source/modules/memories/naive_textual_memory.md
@@ -3,11 +3,9 @@ title: "NaiveTextMemory: Simple Plain Text Memory"
desc: "The most lightweight memory module in MemOS, designed for rapid prototyping and simple scenarios. No vector database required—quickly retrieve memories using keyword matching."
---
-# NaiveTextMemory: Simple Plain Text Memory
+Let's get started with the MemOS memory system in the simplest way possible!
-Let's start using the MemOS memory system in the simplest way possible!
-
-**NaiveTextMemory** is a lightweight, in-memory plain text memory module that stores memories in a memory list and uses keyword matching for retrieval. It's the best starting point for learning MemOS and is suitable for demos, testing, and small-scale applications.
+NaiveTextMemory is a lightweight, memory-based, plain-text memory module. It stores memories in an in-memory list and retrieves them using keyword matching. It is the perfect starting point for learning MemOS, as well as an ideal choice for demos, testing, and small-scale applications.
## Table of Contents
@@ -62,7 +60,7 @@ By the end of this guide, you will be able to:
- Keyword search scenarios (queries directly match memories)
::
-::alert{type="warning"}
+::note
**Performance Tip**
When memory count exceeds 1000, it's recommended to upgrade to [GeneralTextMemory](/open_source/modules/memories/general_textual_memory), which uses vector search for better performance.
::
@@ -139,19 +137,8 @@ Sort all memories by match count in descending order
#### Step 4: Return Results
Return the top-k memories as search results
-::
-
-**Algorithm Comparison**
-
-| Feature | Keyword Matching (NaiveTextMemory) | Vector Semantic Search (GeneralTextMemory) |
-| ------------------ | ---------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------ |
-| **Semantic Understanding** | ❌ Doesn't understand synonyms | ✅ Understands similar concepts |
-| **Resource Usage** | ✅ Extremely low | ⚠️ Requires embedding model and vector DB |
-| **Execution Speed** | ✅ Fast (O(n)) | ⚠️ Slower (indexing + querying) |
-| **Suitable Scale** | < 1K memories | 10K - 100K memories |
-| **Predictability** | ✅ Intuitive results | ⚠️ Black box model |
-::alert{type="info"}
+::note
**Example Comparison**
Query: "cat"
- **Keyword Matching**: Only matches memories containing "cat"
@@ -238,7 +225,7 @@ memory.add(memories)
print(f"✓ Added {len(memories)} memories")
```
-::alert{type="info"}
+::note
**Advanced: Using MultiModal Reader**
If you need to process multimodal content such as images, URLs, or files, use `MultiModalStructMemReader`.
View complete example: [Using MultiModalStructMemReader (Advanced)](./tree_textual_memory#using-multimodalstructmemreader-advanced)
@@ -332,7 +319,7 @@ if memories:
# memory.delete_all()
```
-::alert{type="info"}
+::note
**Extension: Internet Retrieval**
NaiveTextMemory focuses on local memory management. For retrieving information from the internet and adding it to your memory store, see:
[Retrieve Memories from the Internet (Optional)](./tree_textual_memory#retrieve-memories-from-the-internet-optional)
@@ -367,7 +354,7 @@ When calling `dump(dir)`, the system saves memories to:
Use `load(dir)` to fully restore all memory data.
-::alert{type="warning"}
+::note
**Important Note**
Memories are stored in memory and will be lost after process restart. Remember to call `dump()` regularly to save data!
::
diff --git a/content/en/open_source/modules/memories/neo4j_graph_db.md b/content/en/open_source/modules/memories/neo4j_graph_db.md
index 455f8078..1de5bcb9 100644
--- a/content/en/open_source/modules/memories/neo4j_graph_db.md
+++ b/content/en/open_source/modules/memories/neo4j_graph_db.md
@@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
---
-title: Graph Memory Backend
+title: Neo4j Graph Database
desc: "This module provides graph-based memory storage and querying for memory-augmented systems such as RAG, cognitive agents, or personal memory assistants.
It defines a clean abstraction (`BaseGraphDB`) and includes a production-ready implementation using **Neo4j**."
---
@@ -185,4 +185,4 @@ You can add support for any other graph engine (e.g., **TigerGraph**, **DGraph**
* `GraphDBConfigFactory.backend_to_class`
* `GraphStoreFactory.backend_to_class`
-See `src/memos/graph_dbs/neo4j.py` as a reference implementation.
+See `src/memos/graph_dbs/neo4j.py` as a reference for implementation.
diff --git a/content/en/open_source/modules/memories/overview.md b/content/en/open_source/modules/memories/overview.md
index 35ab4e47..a90e7d67 100644
--- a/content/en/open_source/modules/memories/overview.md
+++ b/content/en/open_source/modules/memories/overview.md
@@ -3,19 +3,18 @@ title: "Memory Modules Overview"
desc: "Complete guide to MemOS memory systems - from lightweight text memory to advanced graph structures, choose the right memory module for your needs"
---
-# Memory Modules Overview
-MemOS provides a rich set of memory modules to meet various needs from rapid prototyping to production environments. This guide helps you quickly find the most suitable memory solution.
+The Memory Module provides Agents with essential long-term memory capabilities. Instead of acting as a static database, it mimics human cognitive processes by automatically extracting, organizing, and linking information. Choosing different memory modules allows you to customize and enhance your Agent's skills.
## 🎯 Quick Selection Guide
::alert{type="info"}
**Not sure which to choose?** Follow this decision tree:
-- 🚀 **Quick testing/demo** → [NaiveTextMemory](#naivetextmemory-simple-textual-memory)
-- 📝 **General text memory** → [GeneralTextMemory](#generaltextmemory-general-purpose-textual-memory)
-- 👤 **User preference management** → [PreferenceTextMemory](#preferencetextmemory-preference-memory)
-- 🌳 **Structured knowledge graph** → [TreeTextMemory](#treetextmemory-hierarchical-structured-memory)
-- ⚡ **Inference acceleration** → [KVCacheMemory](#kvcachememory-activation-memory)
+- 🚀 **Quick testing/demo**: Get started easily with no additional software → [NaiveTextMemory](#naivetextmemory-simple-textual-memory)
+- 📝 **General text memory**: Retain chat history or massive documents with semantic search capabilities → [GeneralTextMemory](#generaltextmemory-general-purpose-textual-memory)
+- 👤 **User preference management**:Specifically designed for building and managing user profiles → [PreferenceTextMemory](#preferencetextmemory-preference-memory)
+- 🌳 **Structured knowledge graph**: Ideal for data with complex logical relationships and interconnections → [TreeTextMemory](#treetextmemory-hierarchical-structured-memory)
+- ⚡ **Inference acceleration**: Optimized for high-traffic scenarios to ensure stable and rapid responses → [KVCacheMemory](#kvcachememory-activation-memory)
::
---
diff --git a/content/en/open_source/modules/memories/polardb_graph_db.md b/content/en/open_source/modules/memories/polardb_graph_db.md
index 1a58e416..19ff756f 100644
--- a/content/en/open_source/modules/memories/polardb_graph_db.md
+++ b/content/en/open_source/modules/memories/polardb_graph_db.md
@@ -1,11 +1,9 @@
---
title: "PolarDB Graph Database"
-desc: "Configuration and usage of PolarDB graph database in the MemOS framework"
+desc: "Configuration and usage of PolarDB graph database in the MemOS framework. MemOS supports using **PolarDB** (based on Apache AGE extension) as a graph database backend for storing and retrieving knowledge graph-style memory data. PolarDB combines the powerful capabilities of PostgreSQL with the flexibility of graph databases, making it particularly suitable for scenarios requiring both relational and graph data queries."
---
-# PolarDB Graph Database
-MemOS supports using **PolarDB** (based on Apache AGE extension) as a graph database backend for storing and retrieving knowledge graph-style memory data. PolarDB combines the powerful capabilities of PostgreSQL with the flexibility of graph databases, making it particularly suitable for scenarios requiring both relational and graph data queries.
## Features
diff --git a/content/en/open_source/modules/memories/preference_textual_memory.md b/content/en/open_source/modules/memories/preference_textual_memory.md
index d16763fd..ab715be5 100644
--- a/content/en/open_source/modules/memories/preference_textual_memory.md
+++ b/content/en/open_source/modules/memories/preference_textual_memory.md
@@ -49,9 +49,8 @@ desc: "`PreferenceTextMemory` is a textual memory module in MemOS for storing an
- Learning assistance systems (adapting to learning styles)
::
-::alert{type="info"}
-**Applicable Scenarios**
-When you need to build systems that can "remember" user preferences and provide personalized services accordingly, `PreferenceTextMemory` is the best choice.
+
+In conclusion, when you need to build systems that can "remember" user preferences and provide personalized services accordingly, `PreferenceTextMemory` is the best choice.
::
## Core Concepts and Workflow
@@ -74,7 +73,7 @@ Preference memory can be divided into explicit preference memory and implicit pr
- User frequently requests detailed explanations → prefers in-depth understanding
- User mentions environmental topics multiple times → concerned about sustainable development
-::alert{type="success"}
+::note
**Intelligent Extraction**
`PreferenceTextMemory` automatically extracts both explicit and implicit preferences from conversations using LLM, no manual annotation required!
::
diff --git a/content/en/open_source/modules/memories/tree_textual_memory.md b/content/en/open_source/modules/memories/tree_textual_memory.md
index 9bf430d7..10b0862e 100644
--- a/content/en/open_source/modules/memories/tree_textual_memory.md
+++ b/content/en/open_source/modules/memories/tree_textual_memory.md
@@ -1,12 +1,12 @@
---
title: "TreeTextMemory: Structured Hierarchical Textual Memory"
----
-
-Let’s build your first **graph-based, tree-structured memory** in MemOS!
+desc: "Let’s build your first **graph-based, tree-structured memory** in MemOS!
**TreeTextMemory** helps you organize, link, and retrieve memories with rich context and explainability.
-[Neo4j](/open_source/modules/memories/neo4j_graph_db) is the current backend, with support for additional graph stores planned in the future.
+[Neo4j](/open_source/modules/memories/neo4j_graph_db) is the current backend, with support for additional graph stores planned in the future."
+---
+
## Table of Contents
@@ -309,7 +309,7 @@ for m_list in mixed_memories:
print(f"✓ Extracted and added {len(mixed_memories)} memories from mixed content")
```
-::alert{type="info"}
+::note
**MultiModal Reader Advantages**
- **Smart Routing**: Automatically identifies content type (image/URL/file) and selects appropriate parser
- **Format Support**: Supports PDF, DOCX, Markdown, HTML, images, and more
@@ -318,7 +318,7 @@ print(f"✓ Extracted and added {len(mixed_memories)} memories from mixed conten
- **Context Preservation**: Uses sliding window to maintain context continuity between chunks
::
-::alert{type="tip"}
+::note
**Configuration Tips**
- Use the `direct_markdown_hostnames` parameter to specify which domains should return Markdown format
- Supports both `mode="fast"` and `mode="fine"` extraction modes; fine mode extracts more details
diff --git a/content/en/settings.yml b/content/en/settings.yml
index 8abeb961..d96bedf3 100644
--- a/content/en/settings.yml
+++ b/content/en/settings.yml
@@ -37,15 +37,15 @@ nav:
- "(ri:github-line) Open Source":
- "(ri:rocket-line) Getting Started":
- - "(ri:install-line) Installation": open_source/getting_started/installation.md
+ - "(ri:install-line) Installation Guide": open_source/getting_started/installation.md
- "(ri:bookmark-line) Your First Memory": open_source/getting_started/your_first_memory.md
- "(ri:lightbulb-line) Core Concepts": open_source/home/core_concepts.md
- "(ri:building-2-line) Architecture": open_source/home/architecture.md
- "(ri:file-code-line) REST API Server": open_source/getting_started/rest_api_server.md
- - "(ri:code-line) Examples": open_source/getting_started/examples.md
+ - "(ri:code-line) MemOS Examples": open_source/getting_started/examples.md
- "(ri:cpu-line) MOS":
- - "(ri:eye-line) Overview": open_source/modules/mos/overview.md
+ - "(ri:eye-line) API Development Guide": open_source/modules/mos/overview.md
- "(ri:checkbox-multiple-blank-line) MemCube": open_source/modules/mem_cube.md
- "(ri:book-open-line) MemReader": open_source/modules/mem_reader.md
- "(ri:calendar-line) MemScheduler": open_source/modules/mem_scheduler.md
@@ -54,7 +54,7 @@ nav:
- "(ri:brain-line) Memories":
- - "(ri:database-2-line) Overview": open_source/modules/memories/overview.md
+ - "(ri:database-2-line) Memory Modules Overview": open_source/modules/memories/overview.md
- "(ri:book-2-line) Plaintext Memory":
- "(ri:file-text-line) Naive Textual Memory": open_source/modules/memories/naive_textual_memory.md
- "(ri:file-text-line) General Textual Memory": open_source/modules/memories/general_textual_memory.md
@@ -67,17 +67,17 @@ nav:
- "(ri:star-line) Best Practice":
- "(ri:speed-line) Performance Tuning": open_source/best_practice/performance_tuning.md
- - "(ri:wifi-line) Network Workarounds": open_source/best_practice/network_workarounds.md
+ - "(ri:wifi-line) Network Environment Adaptation": open_source/best_practice/network_workarounds.md
- "(ri:error-warning-line) Common Errors & Solutions": open_source/best_practice/common_errors_solutions.md
- - "(ri:tools-line) MCP for Coze Space and Tools": open_source/best_practice/mcp_for_cozespace_and_tools.md
+ - "(ri:tools-line) Configuring Memos MCP in Coze Space": open_source/best_practice/mcp_for_cozespace_and_tools.md
- "(ri:heart-line) Contribution":
- - "(ri:eye-line) Overview": open_source/contribution/overview.md
+ - "(ri:eye-line) Contributing to MemOS": open_source/contribution/overview.md
- "(ri:tools-line) Setting Up": open_source/contribution/setting_up.md
- "(ri:git-branch-line) Development Workflow": open_source/contribution/development_workflow.md
- "(ri:git-commit-line) Commit Guidelines": open_source/contribution/commit_guidelines.md
- - "(ri:article-line) Writing Docs": open_source/contribution/writing_docs.md
- - "(ri:flask-line) Writing Tests": open_source/contribution/writing_tests.md
+ - "(ri:article-line) Documentation Writing Guidelines": open_source/contribution/writing_docs.md
+ - "(ri:flask-line) How to Write Unit Tests": open_source/contribution/writing_tests.md
- "(ri:file-code-line) API Reference": api-reference/search-memories