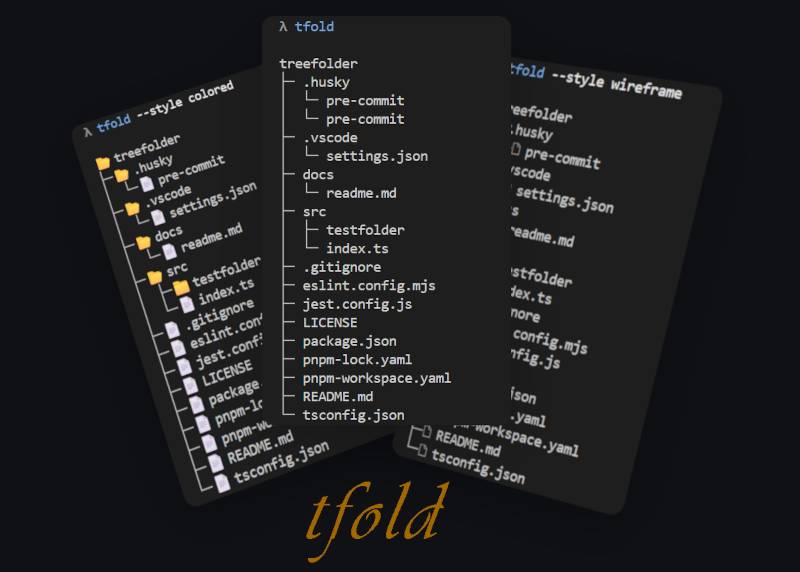
A node.js CLI utility generating a tree representation (treeview) of a folder structure including its contained files and subfolders.
This CLI tool requires node.js or a compatible JavaScript runtime environment to execute successfully. npm, pnpm or yarn may be required as well, in case you'd like to install the tool manually and/or to modify the source code.
This is the recommanded and easiest approach.
-
Install using
pnpm(see below),yarnornpm:pnpm add --global @khatastroffik/treefolder
-
start using the CLI tool from any directory:
# show treeview of the current directory tfold # or show treeview of any directory tfold <some-path-to-be-used-as-tree-root>
Note: you may configure the tool using some options as needed. See the Features list.
- Auto "root folder"
- Auto "ignore paths"
- Sort leaves "folders first"
- List output
- Styled output
- Version information
- Extended help / man page
- Verbose output
- Debug Output
- Limit the maximum amount of processed items / limit the output size
- Clear screen (command line stdout) forehand
- Set default options/flags per env variables (todo)
- Auto update (in evaluation)
If not specified as a command line argument, the "root folder" of the tree is set to the current working directory aka ..
This tool is intentionally ignoring i.e. filtering out a few folder or file items by default and won't proceed with such ignored items i.e. those won't be visible in the resulting treeview.
The following paths (within the root folder) are ignored by default: node_modules , dist, build, .git, .husky\_, logs, .angular and coverage.
Notes:
- Glob-syntax is not supported at the moment. The ignored paths are matching real folder paths, starting within i.e. resolved into the root folder.
- This filtering cannot be disabled or modified at the moment. Feel free to edit the ignored paths/items directly in the source code of the tool, when suitable.
By default, the list or the leaves of the treeview are sorted following the "folders first" principle: All the folders are listed first, then all the files. All items are alphabetically sorted. This apply at any depth within the tree structure.
This behavior can be disabled using the command line argument --unsorted or -u. In this case, all items are sorted the way the operating system does by default e.g. sorted by their names, regardless of their type (directory or file).
When the command line argument --list or -l is used, all the folders and files will be displayed as a flat list instead of as a treeview.
Note: the command line arguments --unsorted and --style colored may also be applied to refine i.e. adapt the list output. See the List output examples
The treeview i.e. tree representation can be generated and displayed using 4 different styles: none (default), black, wireframe or colored.
The style can be defined using the command line argument --styleor -s like so: --style <name of the style>.
→ Examples of styled output can be found in the additional documentation: Styled output examples
Notes:
- some shell environments may not display the symbols (which are represented using specific unicode code points like
U+1F5BForU+1F5C1) properly. Try to change the font used in the shell or to change the code page used by your shell in the background to interpret the chars, in order to display the unicode symbols properly. - On some shell environments e.g. under Windows OS, the output may still be faulty due to the OS automatically pre-formating the output in an inadequate way. Try to use another shell environment then.
Use the command line argument --version or -v to display the version information about the tool and eventually inform about the availability of an updated version of treefolder.
Note: this flag is having the second highest priority - after the help flag: if set, it will dismiss all other options/flag (but the clear and help flag).
Use the command line argument --help or -h to display detailled instructions and hints about using treefolder in a suitable way.
Note: this flag is having the highest priority: if set, it will dismiss all other options/flag (but the clear flag, which may always be triggered).
When the flag i.e. command line argument --verbose or -b is defined/set, then a few more information will be displayed together with the tree representation.
Use the flag --debug or -d to display additional information about the used tool configuration.
In order to avoid very long processing time and memory consumption/wastage, treefolder defines a default amount of items (folders + files), that may be processed i.e. displayed at once.
The default limit is: 500 items.
If you'd like or await to proceed with more than this limit, then you may rise it using the --max-items or -m command line argument.
The max-items value must be a valid number and must not be below 1 or above 32768.
Treefolder will exit with an error if the (default or manually defined) limit is reached or if the max-items command line argument is not valid.
Use the flag --clear or -c to cleanup the command line (stdout) screen before displaying the result.
-
Clone (e.g. using
git) or download this repository locally in order to make this tool available in your environment.gh repo clone khatastroffik/treefolder # or git clone https://github.com/khatastroffik/treefolder.git -
Navigate to the repo folder:
cd treefolder
-
Install the (dev-) dependencies using your favorite package manager and transpile the TypeScript source code into a JavaScript module.
# first install the development dependencies pnpm install # then transpile the source code to javascript pnpm build
-
Use your favorite package manager to install the tool globally. For example:
npm install -g # or (YES, TWICE IN A ROW!) pnpm link --global pnpm link --globalNote: pnpm link lacks of refinements (!) as of v10.x, but this seems to work well, despite the warnings...
-
Use the CLI tool alias
tfold. E.g.:# in any directory/folder simply run tfold # you may use additional arguments too, in order to configure the output tfold --verbose -s colored /c/DEV/a-folder-to-be-scanned # or tfold c:\\DEV\\another-folder --unsorted --style wireframe
Within the local clone/copy of the treefolder repository, you may:
pnpm tsx src\index.ts
# or
pnpm tsx src\index.ts [root-path] [options]
# or run and watch for code changes
pnpm devor
# at least once
pnpm build
# then
pnpm start
# or
node .
# or
node . ..\..\some-folder
# or
node dist\index.js ..\..\some-folder
# or
node dist\index.js --style=colored --unsorted --verbose c:\test\some-other-folder
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────┐
| |
╭━┳━╭━╭━╮╮
┃┈┈┈┣▄╋▄┫
┃┈┃┈╰━╰━━━━━━╮ "K11K"
╰┳╯┈┈┈┈┈┈┈┈ ◢█◣ a very pragmatic dog
┃┈┈┈┈┈┈┈┈┈┈████
┃┈┈┈┈┈┈┈┈┈┈◥█◤
┃┈┈┈┈╭━┳━━━━╯
┣━━━━━━┫
| |
└──────────── made by khatastroffik ──────────┘